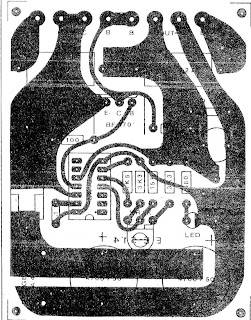
Completed PWM Dimmer/Speed Control
An Electronic Circuits Blog with Latest and rear Electronic Circuits for Hobby and Projects
Thursday, December 27, 2012
Motor Speed Controller | PWM Controller for Dimmer or Motor Speed Controller
This is yet another project born of necessity. It's a simple circuit,
but does exactly what it's designed to do - dim LED lights or control
the speed of 12V DC motors. The circuit uses PWM to regulate the
effective or average current through the LED array, 12V incandescent
lamp (such as a car headlight bulb) or DC motor. The only difference
between the two modes of operation is the addition of a power diode for
motor speed control, although a small diode should be used for dimmers
too, in case long leads are used which will create an inductive back EMF
when the MOSFET switches off.
The photo shows what a completed board looks like. Dimensions are 53 x 37mm, so it's possible to install it into quite small spaces. The parts used are readily available, and many substitutions are available for both the MOSFET and power diode (the latter is only needed for motor speed control). The opamps should not be substituted, because the ones used were chosen for low power and their ability to swing the output to the negative supply rail.
Wednesday, December 26, 2012
1W LED Driver Circuit
This circuit is designed to drive the 1W LEDs that are now commonly available. Their non-linear voltage to current relationship and variation in forward voltage with temperature necessitates the use of a 350mA, constant-current power source as provided by this supply. In many respects, the circuit operates like a conventional step-down (buck) switching regulator. Transistor Q1 is the switching element, while inductor L1, diode D1 and the 100mF capacitor at the output form the energy transfer and storage elements. The pass transistor (Q1) is switch-ed by Q2, which together with the components in its base circuit, forms a simple oscillator. A 1nF capacitor provides the positive feedback necessary for oscillation. The output current is sensed by transistor Q3 and the two paralleled resistors in its base-emitter circuit.
Light Dimmer | Automatic Light Dimmer Circuit
In many cases, the dimmer presented here may be built into a wall-mounted box containing the light switch. It is intended for use with 240 V incandescent lamps only. When it is fitted, and the light is switched on, the lamp does not come on fully for about 400 ms (which is not noticeable). When the light is switched off, it stays on unchanged for about 20 s, and then goes out gradually. This has the advantage that it is not immediately dark when the light is switched off. When light switch S1 is turned on, capacitor C2 is charged via R1, C1 and bridge rectifier D1–D4. Zener diode D5 limits the potential across C2 to about 15 V. After a short while, diode D6 lights, whereupon a potential difference ensues across light sensitive resistor R3, which is sufficient to trigger triac Tr1.
Sunday, December 23, 2012
1200 Watt Dimmer | 1200 Watt AC Dimmer by Triac Q4006LT
This is Power AC Dimmer 1200 watt size. It is use a Triac Q4006LT. Friends ever tour is the foreign land has and to ever reach rest a hotel. On bed head has will head bed fire decorates. It has a button opens-close and a button controls the brightness with the equipment this/these be AC Dimmer follow our circuit can fine to decorate.
Saturday, December 22, 2012
Drill Controller | Mini-Drill Controller Circuit
This circuit is intended as a revolution control for small dc motors as fitted, for instance, in small electric drills (such as used for precision engineering and for drilling boards, among others). The behavior of these motors, which are normally permanent magnet types, is comparable to that of independently powered motors. In theory, the rpm of these motors depends solely on the applied voltage.
Tuesday, December 18, 2012
Dimmer Circuit | lamp dimmer Circuit with LM555 and TIP2955
This circuit is DC Dimmer Circuit. By use IC LM555 be model Astable Multi
vibrator. It is can change translate Duty Cycle with fining VR1 and VR2
be formed fine brightness level that want.
Friday, December 14, 2012
Undestanding Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) | PWM Fan controller Circuit
PWM or Pulse Width Modulation has generally been regarded as too complicated for PC fan speed control compared against using rheostats or linear voltage regulators such as the LM317. I present here a PWM circuit that is simple and cheap enough to be built by the casual electronics builder.
Why would you want to use PWM instead of a rheostat or voltage regulator? Well, like most things, each method has it's own strengths and disadvantages:
Rheostats
Pros: Cheap and easy to use.
Cons: Difficult to find suitable rheostats, introduces current limiting causing the fan to fail to start or stall at slow speed settings.
Linear voltage regulators
Pros: Does not have rheostat like current limiting, temperature control can be incorporated.
Cons: Regulator can generate considerable heat which limits the maximum fan power. (The more powerful the fan, the more heat is generated), maximum output voltage to the fan can be several volts less than the supply limiting the maximum cooling from the fan. (A by-pass switch can be fitted to eliminate this problem, but this adds to the complexity of the circuit).
PWM
Pros: As linear voltage regulator, plus comparatively little heat is generated by the circuit allowing higher powered fans to be used, output is virtually 0-100%, eliminating the need for a bypass switch, fans do not stall or fail to start at minimum fan speed.
Cons: The fan speed sensing is disabled, can cause "growling" noises at very low speed settings with some fans.
What is PWM?
Why would you want to use PWM instead of a rheostat or voltage regulator? Well, like most things, each method has it's own strengths and disadvantages:
Rheostats
Pros: Cheap and easy to use.
Cons: Difficult to find suitable rheostats, introduces current limiting causing the fan to fail to start or stall at slow speed settings.
Linear voltage regulators
Pros: Does not have rheostat like current limiting, temperature control can be incorporated.
Cons: Regulator can generate considerable heat which limits the maximum fan power. (The more powerful the fan, the more heat is generated), maximum output voltage to the fan can be several volts less than the supply limiting the maximum cooling from the fan. (A by-pass switch can be fitted to eliminate this problem, but this adds to the complexity of the circuit).
PWM
Pros: As linear voltage regulator, plus comparatively little heat is generated by the circuit allowing higher powered fans to be used, output is virtually 0-100%, eliminating the need for a bypass switch, fans do not stall or fail to start at minimum fan speed.
Cons: The fan speed sensing is disabled, can cause "growling" noises at very low speed settings with some fans.
What is PWM?
Wednesday, December 12, 2012
Overload Protection | Overload Protection Circuit With with Reset Option
The circuit presented here can be used as overload protector with reset option for inverters or as an electronic fuse in AC mains supply. In this overload protection circuit, the mains supply to the load s like refrigerator is routed via the the N/C (normally closed) contacts of relay RL1. In an inverter, the relay contacts could be used as ‘inverter oscillator’ on/off control. Whenever overload occurs, it inhibits inverter oscillator circuit, which, in turn, stops generation of power. In applications like inverters and UPS, the load must not exceed the rated output power since it can cause excess heating of output transformer windings and active driving devices and thereby damage them.
Tuesday, December 11, 2012
RMS Voltage Control Circuit with Opto Triac MOC3021 and BT136
Triac is a power electronic component that conducts in both directions when triggered through gate. Figure below shows a generic working of triac.As it can be seen that at time t1, angle of sinusoid is 45' which means that if we triggered triac at this angle i-e at 45', only shaded blue area will pass through the triac and hence through the load. Observe that shaded blue are has RMS Voltage less than the pure sinusoid. This is the basic principle by which RMS Voltage control is accomplished. Firing needs a small pulse at gate that can be give through microcontroller also. Similarly at firing angle 90' (firing angle is an angle with reference zero crossing at which the triac is triggered using gate pulse) , only red part of sinusoid will pass through the triac giving us the RMS 110V for 220V.
DC Regulator Circuit | 12V -10A Regulator with IC 723+2N3055
This is circuit regulator 12V 10A by IC 723+2N3055.Q 2N3055 x 2 for to increase form IC LM723.To use transformer 10A, Transistor to Hold Heat-sink.To adjust the output voltage simplyt by VR1 – 1K.
Monday, December 10, 2012
Automotive Speed Indicator | Speed Indicator Circuit for Auto Mobiles
The speed of an automobile can be indicated by detecting the pulses generated by the ignition system and causing an LED to light. The circuit utilizes a quad NOR gate IC chip. Two of the gates are configured as a one shot multivibrator which produces a fixed duration pulse each time the primary circuit of the automobile ignition system opens the circuit to the ignition coil.


Sunday, December 9, 2012
Mains LED | Mains operated LED lamp Circuit
This is a very simple and cost effective mains operated LED lamp which gives a very bright white light.Since no transformer is used, the circuit is very compact and light weight.The mains supply is given to the bridge rectifier via the parallel network formed between R1 and C1.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Featured Posts
Home Electric Circuits
Electric energy required to operate home electric appliances is obtained from the national electric grid. Electric energy generated by ...

Popular Posts
-
By using this Inverter circuit you can convert the 12V dc in to the 220V Ac. In this circuit 4047 is use to generate the square wave of 50Hz...
-
The numeric water level indicator circuit works off 5V regulated power supply. It is built around priority encoder IC 74HC147 (IC1), BCD-to-...